Popular Articles
- Earliest molecular events of vision revealed
- Dynamics and Kinetics in Structural Biology
- XFEL Pulses Demonstrate How Plants Perceive Light
- Structural biology is solved -- now what?
- BioXFEL Postdoctoral Fellowship Award
Archived Articles
News
- Details
- Tuesday, 31 January 2017
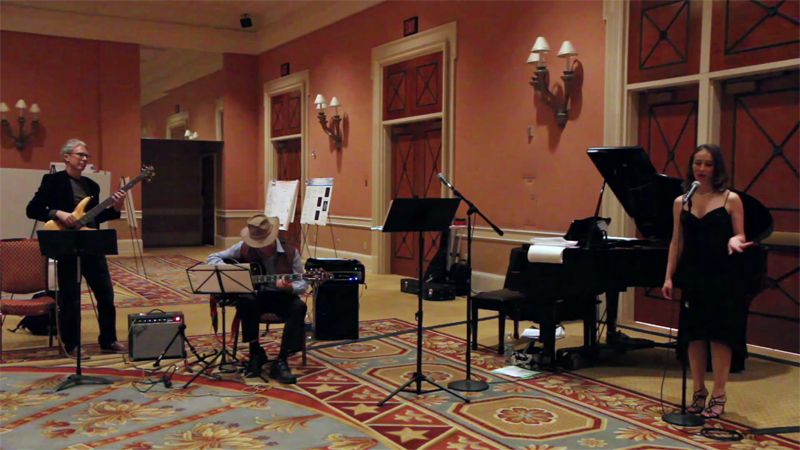

The BioXFEL Jazz Trio headlined the 4th Annual BioXFEL International Conference at Caesar’s Palace featuring John C. H. Spence (piano, guitar, flute), Uwe Weierstall (bass), and Nadia Zatsepin (piano, vocals). The performance included pieces by Gershwin, Bolling, Chopin, and more! Don’t miss footage of their live performance on our YouTube channel!
- Details
- Tuesday, 31 January 2017
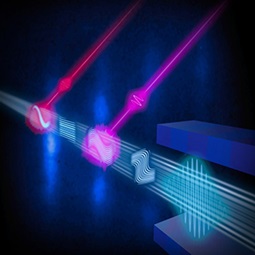
The Science
New electronic devices and energy solutions depend on scientists clearly seeing atoms and molecules at work. Modern x-ray free-electron lasers do just that using electrons to produce intense x-ray pulses that provide atomic-resolution snapshots. To produce stable, organized pulses, scientists demonstrated a new scheme called echo-enabled harmonic generation (EEHG) at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
- Details
- Thursday, 26 January 2017
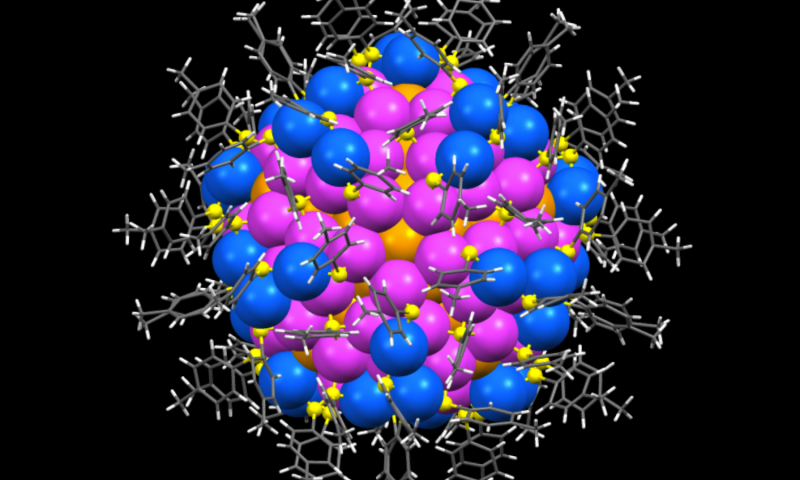
Chemists at Carnegie Mellon University have demonstrated that synthetic nanoparticles can achieve the same level of structural complexity, hierarchy and accuracy as their natural counterparts - biomolecules. The study, published in Science, also reveals the atomic-level mechanisms behind nanoparticle self-assembly.
- Details
- Tuesday, 24 January 2017
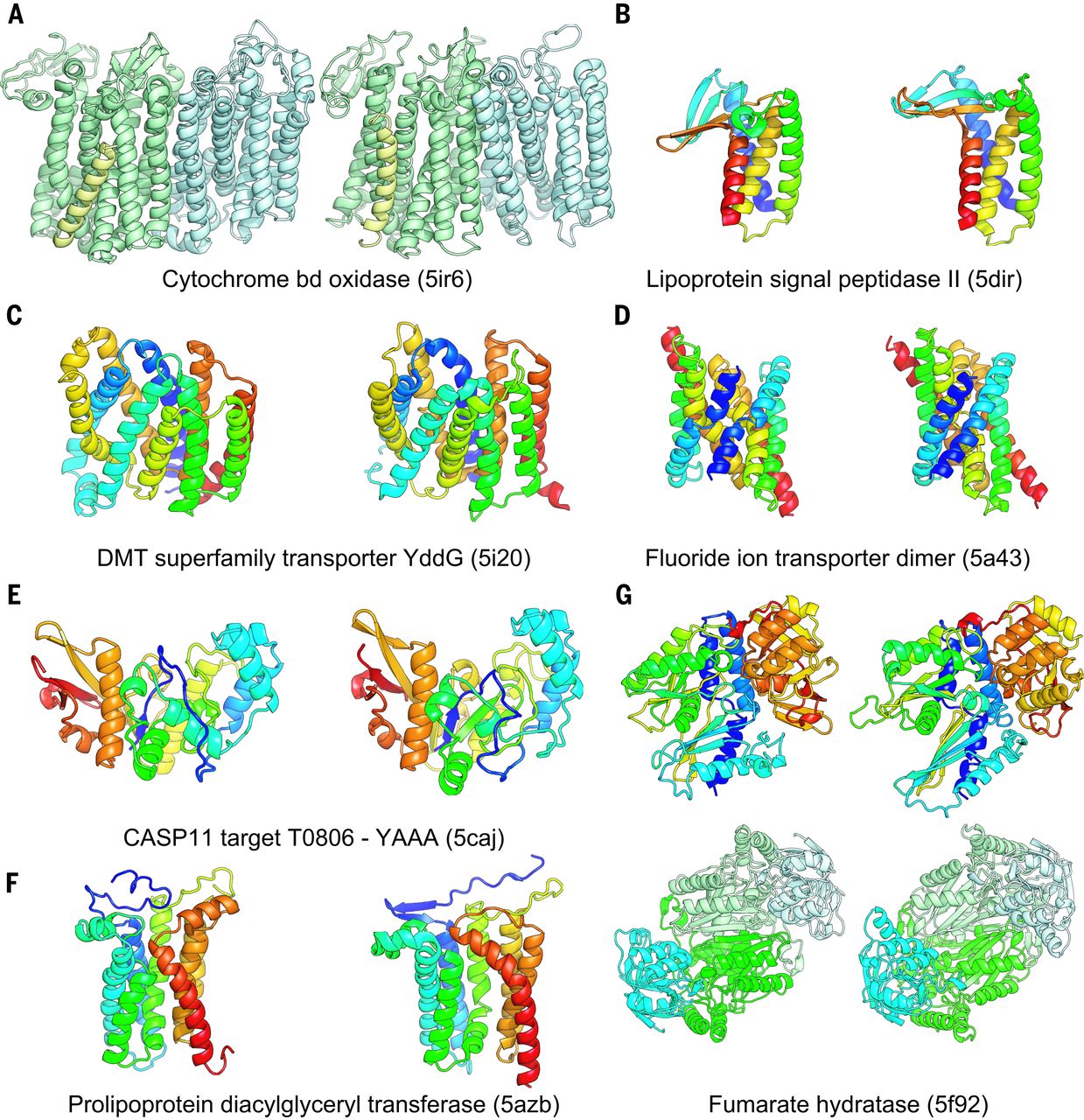
DNA sequence data collected from assorted environments has helped researchers generate 3-D models of more than 600 protein families for which the structures were previously unknown, according to a paper published in Science today (January 19). The metagenomic data enabled protein sequence comparisons across an array of species, which lent a statistical power to the predictions that would otherwise not have been possible.
- Details
- Tuesday, 17 January 2017
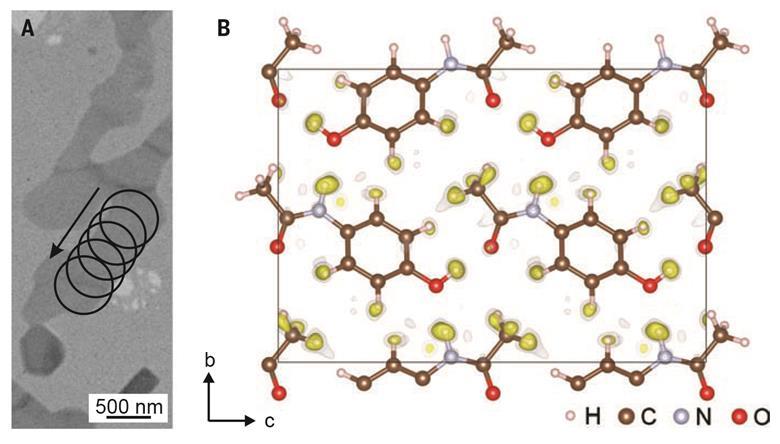
A new algorithm created by Czech and French researchers allows 3D electron diffraction patterns to reveal nanocrystal structures down to the positions of individual hydrogen atoms. Researchers believe its uses could range from studying pharmaceuticals to catalysis and beyond.
- Details
- Monday, 16 January 2017
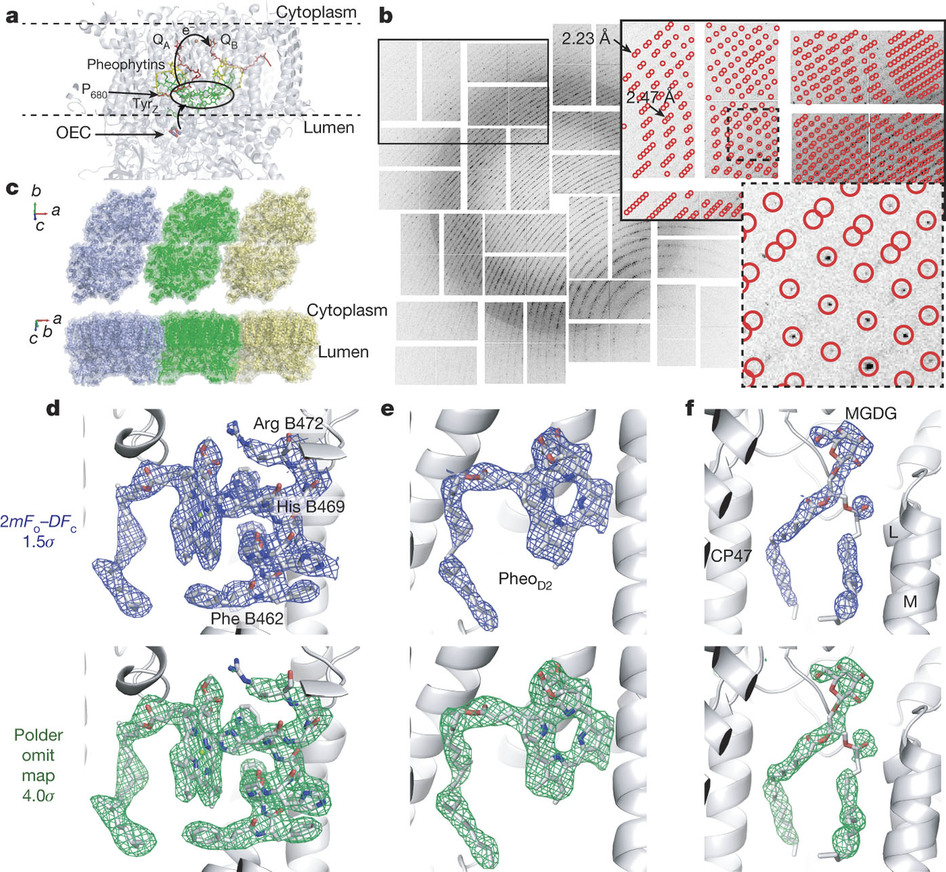
A mystery that has perplexed scientists for centuries may soon be unraveling.
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have captured for the first time how a protein complex—photosystem II—harvests energy from sunlight and uses it to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, a process that generates the oxygen in the atmosphere.





