Popular Articles
- Earliest molecular events of vision revealed
- Dynamics and Kinetics in Structural Biology
- XFEL Pulses Demonstrate How Plants Perceive Light
- Structural biology is solved -- now what?
- BioXFEL Postdoctoral Fellowship Award
Archived Articles
News
- Details
- Thursday, 18 May 2017
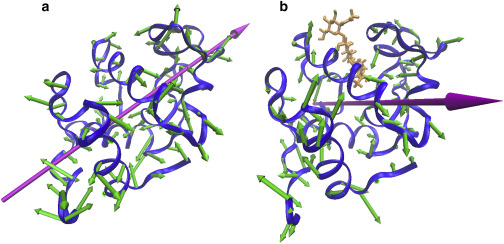
Nearly all protein functions require structural change, such as enzymes clamping onto substrates, and ion channels opening and closing. These motions are a target for possible new therapies; however, the control mechanisms are under debate. Calculations have indicated protein vibrations enable structural change. However, previous measurements found these vibrations only weakly depend on the functional state.
- Details
- Tuesday, 02 May 2017
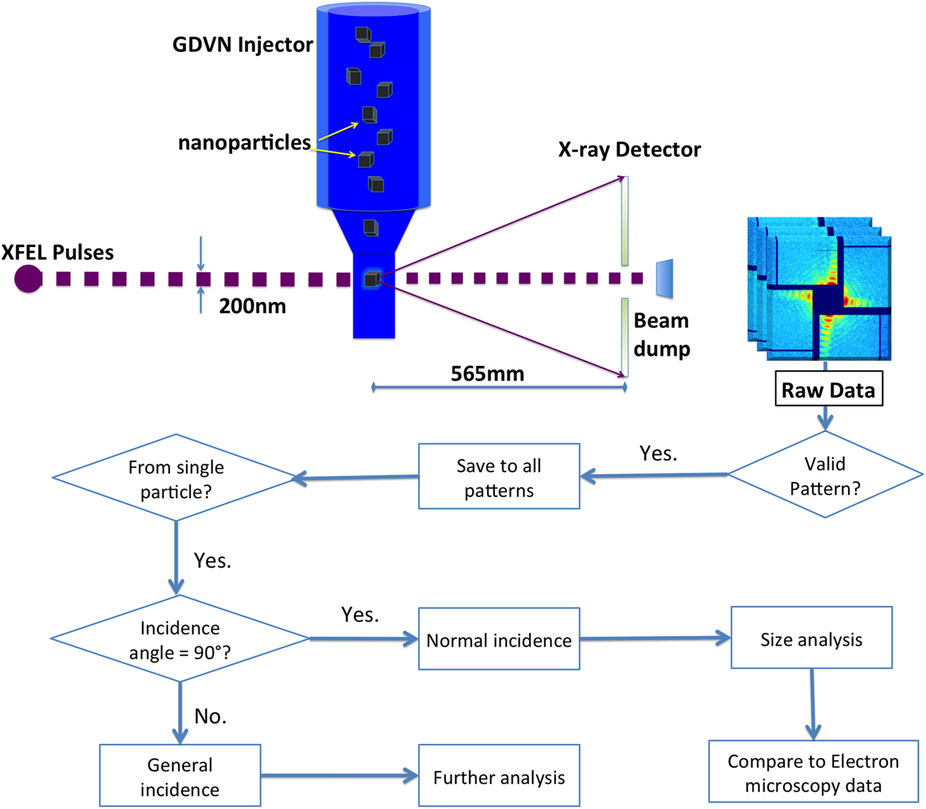
X-ray free-electron lasers provide novel opportunities to conduct single particle analysis on nanoscale particles. Coherent diffractive imaging experiments were performed at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS), SLAC National Laboratory, exposing single inorganic core-shell nanoparticles to femtosecond hard-X-ray pulses.
- Details
- Thursday, 27 April 2017

Abbas Ourmazd, a UWM distinguished professor of physics, has been appointed to serve on the Basic Energy Sciences Advisory Committee (BESAC) of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). The 25-member committee has a substantial impact on national scientific programs, supporting more than 2,500 principal investigators in physics, chemistry, geology and biosciences at 165 institutions in 49 states and 14 DOE laboratories.
- Details
- Thursday, 20 April 2017
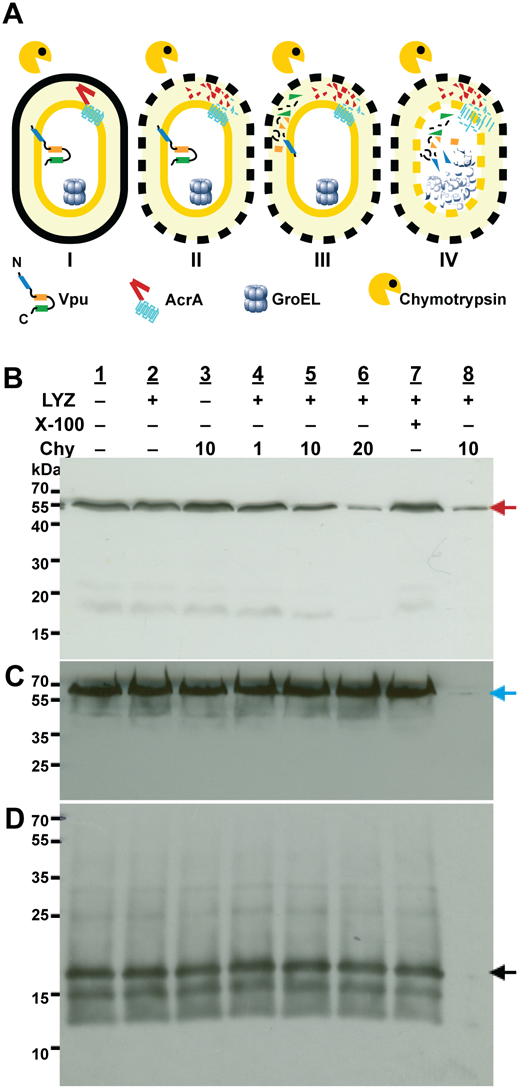
Structural analysis of membrane proteins has traditionally been bottlenecked by the lack of sufficiently large amounts of pure, properly folded and functional membrane proteins. The issue is particularly important considering the fact that membrane proteins constitute a significant proportion of clinical drug targets.
- Details
- Tuesday, 11 April 2017

DESY scientist Henry Chapman has been awarded the Roentgen Medal by the city of Remscheid. The town in which Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen was born has been presenting this award annually since 1951 to individuals who have made outstanding contributions towards improving and advancing the use of the radiation discovered by Roentgen. Henry Chapman, a Leading Scientist at DESY and professor at the University of Hamburg, has been awarded the Medal in recognition of his pioneering work on the application of X-ray lasers for determining the structure of biological macromolecules.
- Details
- Tuesday, 11 April 2017
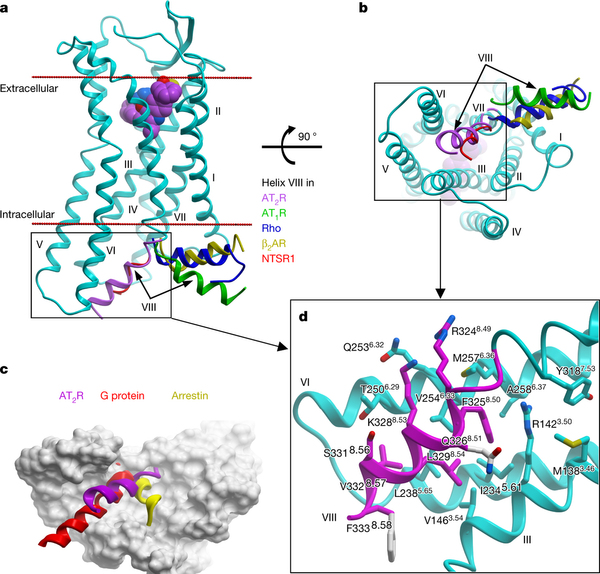
Designing molecules that selectively bind to a specific receptor type is often challenging, but can be crucial for different therapeutic purposes. Both angiotensin II receptors are important drug targets, since the blockade of AT1R has anti-hypertensive effects, while the modulation of AT2R could be useful for cardioprotection, neuropathic pain relief and the treatment of several other conditions.
More Articles...
- The room temperature crystal structure of a bacterial phytochrome determined by serial femtosecond crystallography
- Crystallization of Membrane Proteins in Lipidic Mesophases
- NSF BioXFEL STC Postdoctoral Research Award granted to Benjamin Stauch and Ahmad Hosseinizadeh
- Native phasing of x-ray free-electron laser data for a G protein–coupled receptor
- Job Opening: Research Specialist





