Popular Articles
- Earliest molecular events of vision revealed
- Dynamics and Kinetics in Structural Biology
- XFEL Pulses Demonstrate How Plants Perceive Light
- Structural biology is solved -- now what?
- BioXFEL Postdoctoral Fellowship Award
Archived Articles
News
- Details
- Thursday, 22 June 2017

X-ray crystallography, the workhorse of structural biology, has been revolutionized by the advent of serial femtosecond crystallography using X-ray free electron lasers. Here, the fast pace and history of discoveries are discussed together with current challenges and the method's great potential to make new structural discoveries, such as the ability to generate molecular movies of biomolecules at work.
- Details
- Thursday, 08 June 2017
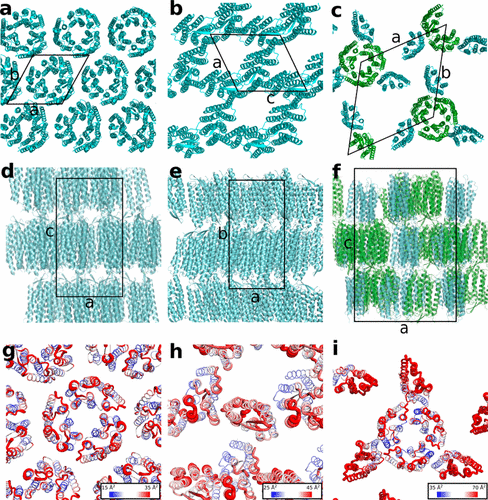
Cherezov lab members in association with researchers from The Scripps Research Institute, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, and Institute of Complex Systems have designed, synthesized, and characterized a series of chemically stable lipids resistant to hydrolysis capable of forming a lipidic cubic phase. The phase properties and lattice parameters of mesophases made of two most promising lipids were characterized. One of these lipids was used for crystallization and structure determination of a prototypical membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin at 4 and 20 °C.
- Details
- Tuesday, 06 June 2017
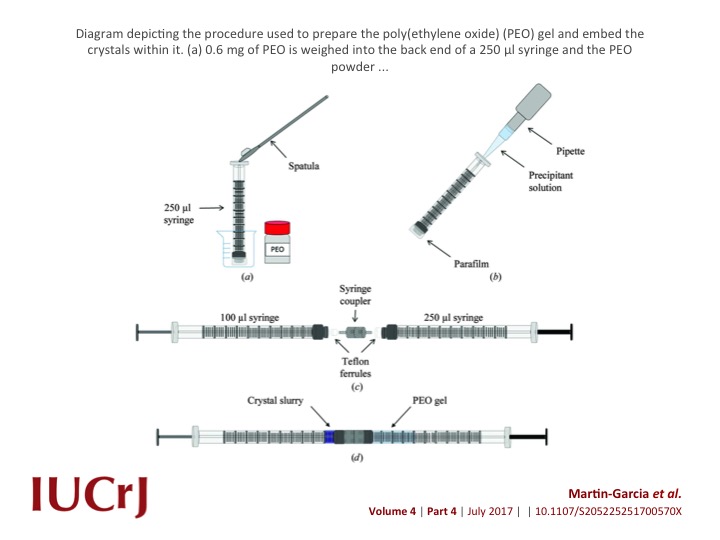
Crystal structuredetermination of biological macromolecules using the novel technique of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) is severely limited by the scarcity of X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) sources. However, recent and future upgrades render microfocus beamlines at synchrotron-radiation sources suitable for room-temperature serial crystallography data collection also.
- Details
- Wednesday, 31 May 2017
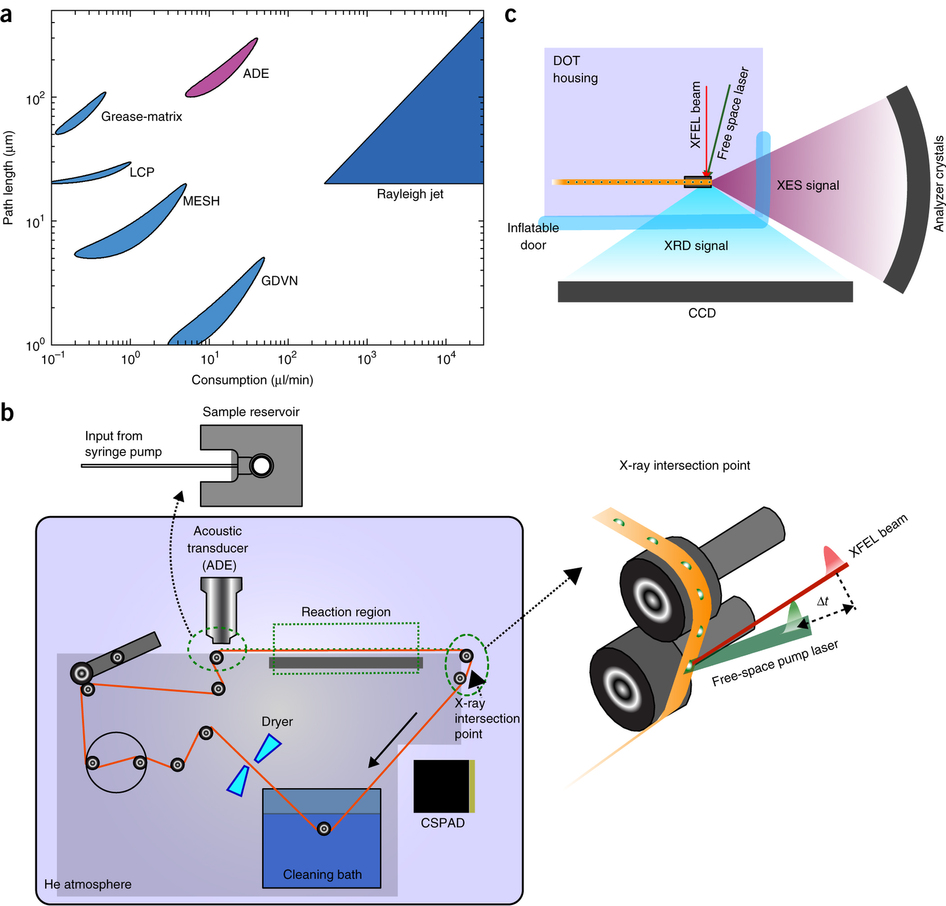
X-ray crystallography at X-ray free-electron laser sources is a powerful method for studying macromolecules at biologically relevant temperatures. Moreover, when combined with complementary techniques like X-ray emission spectroscopy, both global structures and chemical properties of metalloenzymes can be obtained concurrently, providing insights into the interplay between the protein structure and dynamics and the chemistry at an active site.
- Details
- Tuesday, 30 May 2017
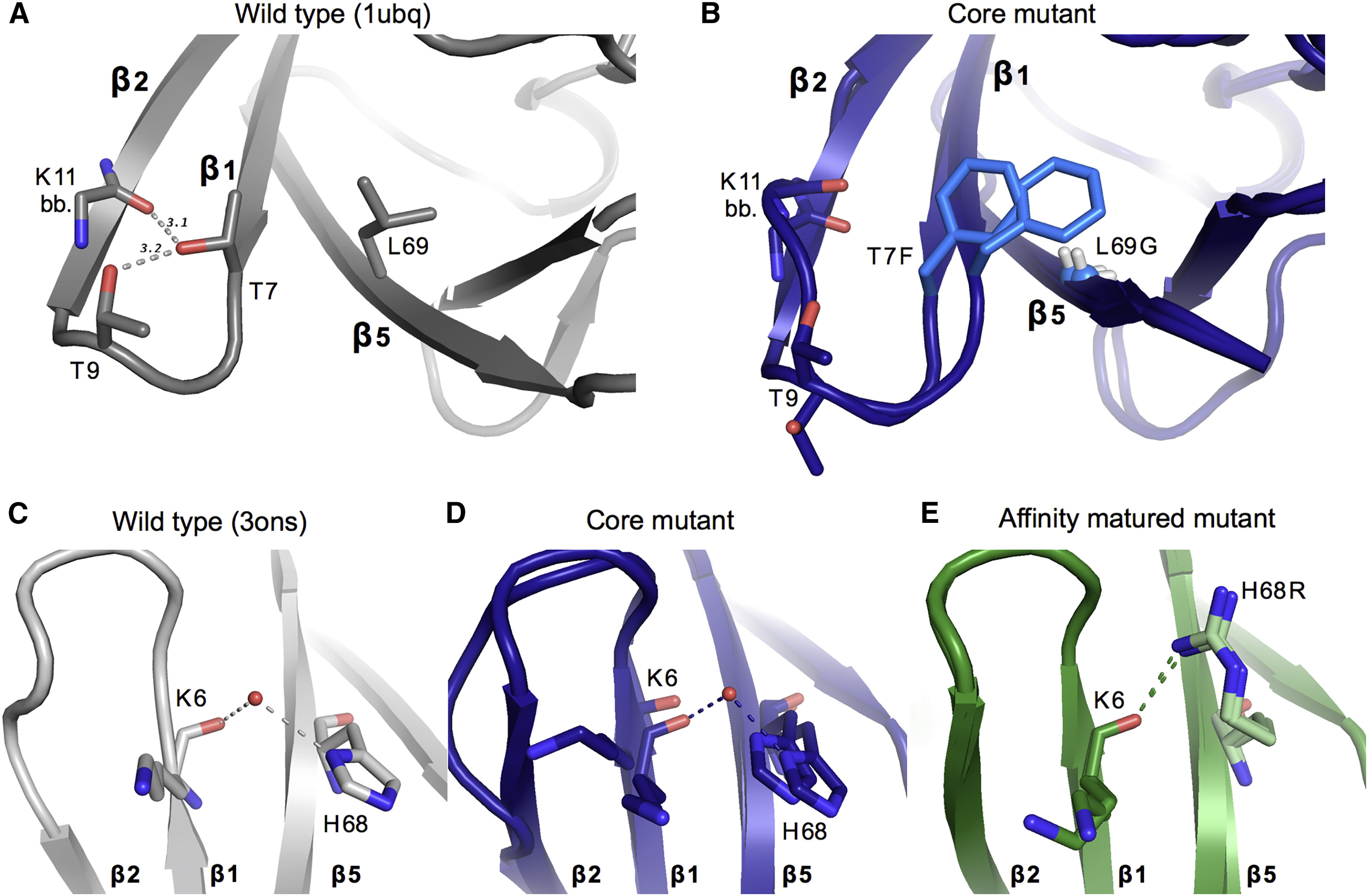
Although protein design has been used to introduce new functions, designed variants generally only function as well as natural proteins after rounds of laboratory evolution. One possibility for this pattern is that designed mutants frequently sample nonfunctional conformations.
- Details
- Tuesday, 23 May 2017
Burrowed deep under the foothills near Palo Alto, Calif., scientists scurried through an underground laboratory, making final preparations for a series of explosions. THEIR PLAN: blow up tiny crystals of proteins that could reveal one of nature's best-kept secrets—how plant photosynthesis turns light into chemical energy. The potential payoff: a step toward unlimited clean power.
More Articles...
- Moving in the Right Direction: Protein Vibrational Steering Function
- Diffraction data of core-shell nanoparticles from an X-ray free electron laser
- BioXFEL CoPI Appointed to DOE Advisory Committee
- Bacterial expression, correct membrane targeting and functional folding of the HIV-1 membrane protein Vpu using a periplasmic signal peptide
- BioXFEL collaborator Henry Chapman receives 2017 Roentgen Medal





